module 2: ASSESSMENTS
Online Course
HOME
Module 1: APPLIED SCIENCES
Module 2: ASSESSMENTS
Module 3: PROGRAM DESIGN
Module 4: CONSIDERATIONS
Consultation – Par Q
One of the most important parts of the fitness assessment is documentation of the collected data. It is important to write down as much information as possible so that future reference to this material lends to a complete understanding of the information written.
Before testing, complete the following:
Medical History Form
PAR-Q
Exercise History Form
Medical Clearance Form by a physician (if necessary)
Informed Consent or Waiver of Liability
Medical Information, Interests and Goals Setting
The medical information you should gather is simply a review with the client regarding:
Past injuries
Joint problems
Previous surgeries that may affect exercise
Recent illnesses
Any other problems that may be affected with exercise
Physiological assessment
Blood pressure
Heart rate
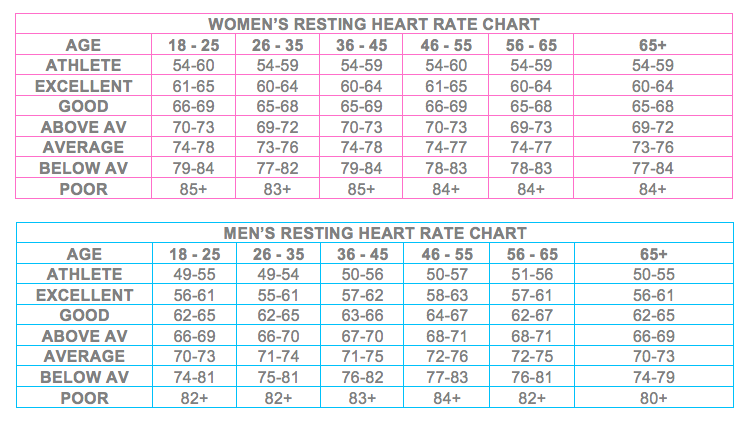
Heart rate can be used as an overall indicator of health and fitness. If resting heart rate is high, it may be an indication of disease or poor physical condition. If heart rate is low, your heart muscle is efficient and pumps more blood with each stroke.
Age Predicted Heart Rate Formula
Heart Rate Intensity Ranges:
*60 – 70% Beginner
*70 – 80% Intermediate
*80 – 90% Advance
Karvonen’s Formula
220- Age = Age-predicted Maximal Heart Rate(Max H. R.)
Max H. R. – Resting Heart Rate ( R. H. R.) = Heart Rate Reserve (H. R. R.)
Heart Rate Reserve (H. R. R.) X Percent of desired intensity (% - %)
+ Resting Heart Rate (R. H. R.) = Karvonen’s T. H. R.
Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
body mass index
Body mass index is used to assess weight relative to height. This technique compares an individual's weight (in kilograms) to their height (in meters, the squared).
BMI Formula: (kg/m2) = WT (in Kg) ÷ HT2 (in m)
[Weight (in lbs.) x 703] ÷ [Height (in inches) squared]
WAIST-TO-HIP RATIO (WHR)
The waist-to-hip ratio is a comparison between the circumference of the waist and the circumference of the hip. This ratio best represents the distribution of body weight, and perhaps body fat, in an individual.
Waist circumference is of greater than 40 inches (102 cm) in men and 35 inches (89 cm) and women are considered strong indicators of abdominal obesity. To calculate the WHR ratio, divide the waist measurement by the hip measurement.
Waist: Measured 1 inch above the navel and below in the xiphoid process.
Hip: measured around the buttocks, above the gluteal fold.
WHR: Waist circumference ÷ hip circumference
Circumference Measurements
Read the circumference to the nearest half of a centimeter. Apply the tape to the site so it is fully extended but not tight. Avoid skin compression or pinching of the skin. Take multiple measurements at each site.
The individual should stand straight but relaxed at all times.
Skinfold measurements
cardiorespiratory assessment
step test
treadmill test
push-up test
Bench Press Test (1 rep / 10 rep)
*The 10 RM is an advisable alternative testing, because it is not advisable to test beginners with maximum resistance lifts. Have the participant completes 10 repetitions with 75% of their maximum resistance. This testing procedure may be a safer means for evaluating muscle strength.







![How+is+BMI+calculated+BMI+is+a+number+calculated+from+a+person%u2019s+height+and+weight.+Formula +weight+(lb)+_+[height+(in)2+]+=+X+703..jpg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/58cd8c39bebafb2e39a48a96/1574795717110-KQMM77B2DATJA7HSFEJ9/How%2Bis%2BBMI%2Bcalculated%2BBMI%2Bis%2Ba%2Bnumber%2Bcalculated%2Bfrom%2Ba%2Bperson%25u2019s%2Bheight%2Band%2Bweight.%2BFormula+%2Bweight%2B%28lb%29%2B_%2B%5Bheight%2B%28in%292%2B%5D%2B%3D%2BX%2B703..jpg)











